Hydraulic Valve ــــ ⏱ 4 min read
Hydraulic Valves are control components in hydraulic systems responsible for regulating the flow, pressure, and direction of hydraulic fluid. These valves are used to manage system performance, safety, and energy efficiency. Below, we will introduce the types, functions, and applications of hydraulic valves:
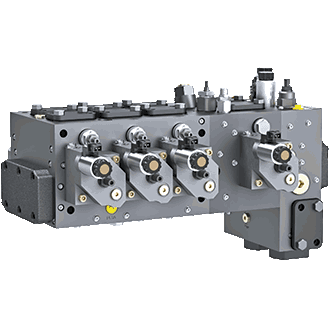
Types of Hydraulic Valves
Hydraulic valves are categorized into three main types based on their function:
- Directional Control Valves:
- Determine the direction of fluid flow (e.g., opening or closing flow paths).
- Common types:
- Spool Valves: Use linear movement of a rod (spool) to change the flow path.
- Poppet Valves: Control flow by opening and closing a disk or cone.
- Applications:
- Controlling cylinders or hydraulic motors (e.g., in excavators).
- Changing the direction of movement in hydraulic systems.
- Pressure Control Valves:
- Regulate or limit system pressure.
- Common types:
- Relief Valve: Releases excess pressure to prevent system damage.
- Pressure Reducing Valve: Reduces output pressure to a specified level.
- Applications:
- Protecting the system from overpressure.
- Adjusting pressure in different parts of the hydraulic circuit.
- Flow Control Valves:
- Regulate the speed of fluid flow (flow rate).
- Common types:
- Needle Valve: Reduces flow rate by changing the cross-sectional area of the flow path.
- Check Valve: Allows flow in one direction and prevents backflow.
- Applications:
- Controlling the speed of cylinders or hydraulic motors.
- Preventing backflow.
Main Components of Hydraulic Valves
- Body: The main structure of the valve.
- Actuator: The mechanism that activates the valve (manual, electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic).
- Poppet/Spool: The moving element that opens or closes the flow path.
- Spring: Returns the valve to its default position.
Applications of Hydraulic Valves
- Heavy Machinery: Cranes, excavators, loaders.
- Automotive Industry: Brake systems, power steering.
- Aerospace Industry: Control of flight surfaces and landing systems.
- Production Lines: Controlling the movement of robots and industrial equipment.
- Energy Systems: Power plants and wind turbines.
Advantages of Hydraulic Valves
- Precise control of pressure, flow rate, and direction.
- High-pressure tolerance (up to 700 bar or more).
- Long lifespan with proper use.
- Flexibility in hydraulic circuit design.
Disadvantages of Hydraulic Valves
- Sensitivity to contamination: Small particles can disrupt valve operation.
- Maintenance costs: Periodic replacement of oil and filters is required.
- Potential leakage: Due to failure of seals or gaskets.
Key Considerations When Selecting a Hydraulic Valve
- Maximum working pressure (in bar or psi).
- Required flow rate (liters per minute or GPM).
- Type of hydraulic fluid (mineral oil, water-oil, etc.).
- Actuation method (manual, electric, pilot).
- Operating temperature (acceptable temperature range).
Examples of Famous Hydraulic Valves
- Parker Valves: For industrial and heavy-duty applications.
- Bosch Rexroth Valves: Advanced technology and high precision.
- Eaton-Vickers Valves: Suitable for high-pressure systems.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- Oil filtration: Preventing contamination from entering the valve.
- Periodic inspection: Checking for wear of internal components.
- Seal replacement: In case of leakage.
- Cleaning: Flushing the valve with clean hydraulic oil.
If you need further details about specific types of valves or their applications, we’d be happy to assist!
افزودن دیدگاه